Pigeons are probably the most familiar of all wild birds. They are found in cities and towns throughout the world and have adapted to living with humans. These birds occur in a variety of habitats, including woodlands, grasslands, and urban areas. Pigeons are gregarious birds and often form large flocks.
Pigeons have a long history of association with humans. The rock dove was the first pigeon domesticated by humans, about 5,000 years ago. Since then, pigeons have been bred for a variety of purposes, including as messenger birds and racing birds. But what exactly are pigeons, and how do they live?
The Biology of Pigeons
Pigeons belong to the bird family Columbidae, which includes doves and other similar species. There are more than 300 different pigeon species in the world. The best known are the rock dove, also called the rock pigeon, and the homing pigeon.
Pigeons have numerous genera and they are classified into the different sub families Columbinae, Treroninae, Gourinae, and Didunculinae.
Columbinae is the largest subfamily and it includes the typical pigeons. These are the smaller species, with short legs and necks. The rock dove, homing pigeons, and owl pigeons are part of this family.
Treroninae is the second-largest subfamily. These pigeons are also called fruit doves or green pigeons. They are found in Africa, Asia, and Oceania. The Fruit Dove and the Nicobar Pigeon are in this family.
Gourinae is a subfamily of Old World pigeons. These are usually called pheasants, or sometimes quail doves. There are only four genera in this group, which includes the White-eyed Pigeon and the Red Turtle Dove.
Didunculinae is the fourth subfamily of pigeons. This group contains a single genus, didunculus, which has only one species: the Tooth-billed Pigeon.
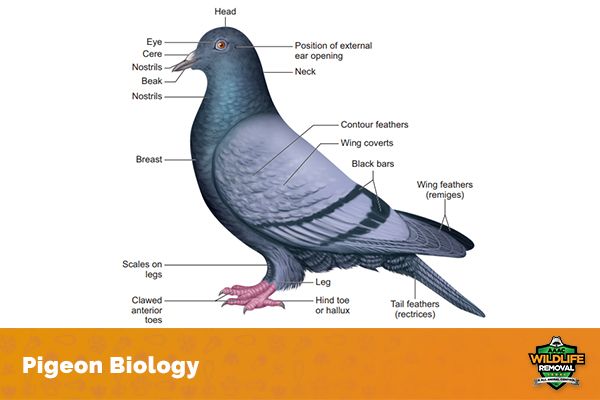
Pigeon Characteristics
Pigeons are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short, legs. They have strong, wing muscles that enable them to fly long distances at high speeds. The wings of pigeons are also adapted for quick changes in direction, which is useful for dodging predators or obstacles.
Pigeons range in size from about 15 centimeters to more than 75 centimeters long. These birds have a smooth, glossy plumage that is usually blue-grey or brownish in colour. Some species have distinct markings, such as the white patches on the wings of feral rock pigeons. Male and female pigeons look alike, but juveniles have duller plumage than adults.
Pigeons are social birds and live in flocks. They communicate with each other using a variety of sounds, including cooing, humming, and hissing.
Pigeon Behaviour
Pigeons are generally diurnal birds, meaning that they are active during the day. However, some species are known to be nocturnal, or active at night.
Pigeons spend a lot of time preening their feathers. This helps to keep their plumage clean and waterproof. Pigeons also use preening as a way to communicate with other members of their flock.
Pigeons are monogamous birds, meaning that they form pairs with one mate and stay with that mate for life. The pair bond between pigeons is very strong, and some pairs have been known to stay together for 20 years or more.
Pigeon Diet
Pigeons are mostly herbivorous birds, meaning that they eat plants. Seeds, fruits, and leaves provide them with the nutrients they need. They also consume grit, which helps them grind up food in their gizzards. Pigeons drink water regularly to stay hydrated.
In addition to their regular diet, pigeons will also eat insects, snails, and small reptiles. This helps them get the protein and other nutrients they need. Pigeons need to eat a balanced diet to stay healthy and active. By eating a variety of different foods, they are able to get all the nutrients they need.
Pigeon Reproduction
Pigeon reproduction is fascinating to watch. The male and female work together to gather nesting materials and build the nest, which is usually made out of twigs, leaves, and grass. Female pigeons lay two eggs, which are incubated by both parents for 18 days.
During this time, the chicks develop inside the egg and are nourished by a yolk sac. When they hatch, the chicks are altricial, meaning that they are born naked and blind. They are also completely dependent on their parents for food and shelter.
The parents feed their chicks with a substance called ‘pigeon milk’. This milk is produced in the crop of the parent birds and is rich in nutrients, which helps the chicks to grow quickly.
Pigeon milk is not actually milk, but a thick solution of pre-digested food that the parents regurgitate into the mouths of their chicks. As the chicks grow older, they begin to explore their surroundings and learn to fly. Once they are independent, they will leave their parents and start their own families.
Wild pigeons seldom live for more than 4 years, while those in captivity can live for up to 20 years.
Pigeon Predators and Threats
Pigeons have a number of predators, including cats, hawks, and snakes. However, the biggest threat to these birds is humans. Pigeons are often considered to be a nuisance by people, and they are killed in large numbers as a result. In addition, pigeons are also hunted for food in some parts of the world.
Pigeon populations have declined in recent years due to these various threats. It is estimated that there are only around 300 million pigeons left in the world today. This is a significant decrease from the estimated 3 billion pigeons that lived in the world just a few hundred years ago.
The decline in pigeon populations is concerning because these birds play an important role in the ecosystem. Pigeons are seed dispersers and help to propagate plants. They are also a food source for many predators. If pigeon populations continue to decline, it could have a negative impact on the environment.
Pigeon Conservation
Despite being killed in large numbers by humans, pigeons are not considered to be endangered. This is because they have a high reproductive rate and are able to adapt to changing environments.
Habitat loss is the biggest threat to this species. Pigeons need access to clean water and a variety of different foods in order to stay healthy. They also need safe places to nest and raise their young.
Pigeon conservation efforts are focused on protecting the habitats of these birds. This includes creating protected areas, planting trees, and restoring degraded habitats. In addition, public education is important in order to raise awareness about the importance of these birds.
Pigeon Breeding
Pigeons are popular pets in many parts of the world. These birds are easy to care for and can be trained to do tricks. Some people even race pigeons.
Domestic pigeon breeding is relatively simple and can be done in your backyard. You will need a pair of pigeons, a nest box, and some food. The pigeons will build their own nest, but you may need to provide them with materials such as straw or twigs.
Once the eggs are laid, they will need to be incubated for 18 days. The parents will take care of this, but you will need to make sure that the nest is kept clean and free from predators.
After the chicks hatch, they will need to be fed pigeon milk for the first few weeks of their lives. Once they are old enough, you can start to wean them onto solid food.
Problem Pigeons
Pigeons are often considered to be pest birds by people. They are attracted to areas where there is food available, and they can quickly become a nuisance if not controlled. Feral pigeons often congregate in large numbers around buildings, parks, and other public places.
This can create problems because pigeons can carry diseases that can be transmitted to humans. In addition, their droppings can contaminate food and water sources. Pigeons can also damage property by roosting on ledges and roofs.
If you have a problem with pigeons, the best thing to do is to contact a professional wildlife control company like AAAC Wildlife Removal. We have the experience and equipment necessary to safely remove pigeons from your property.
Final Word
Pigeons are often considered to be nuisance birds, but they are actually fascinating creatures. These birds play an important role in the ecosystem and if not protected, their populations could decline significantly.
Pigeon conservation efforts are focused on protecting their habitats and raising public awareness about these birds. By working together, we can help to ensure that pigeons are around for future generations to enjoy.
Originally published at AAAC Wildlife Removal: https://aaacwildliferemoval.com/blog/birds/pigeon-biology/













